Abstract
Purpose
The long noncoding RNA LINC00261 was reported to be involved in carcinogenesis and has been validated as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer (PC); however, how LINC00261 is regulated has not been fully examined. Here, we attempted to investigate the upstream and downstream targets of LINC00261 in PC.
Methods
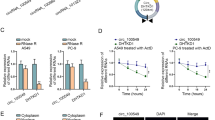
LINC00261 expression in PC tissues was examined by the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets and the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) database. The quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assays were performed to detect the expression level of LINC00261 in PC cells. The location of LINC00261 in PC cells was identified by RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (RNA-FISH). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), cell apoptosis assay, transwell invasion and migration assays testified the critical role of LINC00261 in PC. The luciferase reporter assay was applied to confirm the binding of LINC00261 to its upstream transcription factor KLF13. The changes in LINC00261 related target protein levels were analyzed by Western blotting assay.
Results
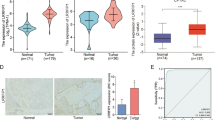
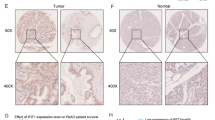
LINC00261 was significantly lower in PC tissues and was mainly concentrated in the nucleus. Overexpression of LINC00261 inhibited the invasion and migration of PC cells. Mechanistically, transcription factor KLF13 was confirmed to inhibit the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process of PC cells by promoting the transcription of LINC00261 and suppressing the expression of metastasis-associated proteins, such as matrix metalloproteinase MMP2 and vimentin, thus inhibiting the metastasis of PC.
Conclusion
LINC00261 regulates PC cell metastasis through the “KLF13-LINC00261-mTOR-P70S6K1-S6” signaling pathway, which provides a significant set of potential PC therapeutic targets.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL, Huarte M. Author Correction: Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):159.
Zhou Q, Zhan H, Lin F, Liu Y, Yang K, Gao Q, Ding M, Liu Y, Huang W, Cai Z. LincRNA-p21 suppresses glutamine catabolism and bladder cancer cell growth through inhibiting glutaminase expression. 2019. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20182372.
Jin Y, Wu P, Zhao W, Wang X, Yang J, Huo X, Chen J, De W, Yang F. Long noncoding RNA LINC00165-induced by STAT3 exerts oncogenic properties via interaction with polycomb repressive complex 2 to promote EMT in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;507(1–4):223–30.
Sahu A, Singhal U, Chinnaiyan AM. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: from function to translation. Trends Cancer. 2015;1(2):93–109.
Al-Rugeebah A, Alanazi M, Parine NR. MEG3: an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019;25(3):859–74.
Soudyab M, Iranpour M, Ghafouri-Fard S. The role of long non-coding rnas in breast cancer. Arch Iran Med. 2016;19(7):508–17.
Yao RW, Wang Y, Chen LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):542–51.
Ma L, Bajic VB, Zhang Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013;10(6):925–33.
Camacho CV, Choudhari R, Gadad SS. Long noncoding RNAs and cancer, an overview. Steroids. 2018;133:93–5.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30.
Ansari D, Tingstedt B, Andersson B, Holmquist F, Sturesson C, Williamsson C, Sasor A, Borg D, Bauden M, Andersson R. Pancreatic cancer: yesterday, today and tomorrow. Future Oncol. 2016;12(16):1929–46.
Yu S, Zhang C, Xie KP. Therapeutic resistance of pancreatic cancer: Roadmap to its reversal. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1875(1):188461.
Ozkan H, Kaya M, Cengiz A. Comparison of tumor marker CA 242 with CA 19–9 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50(53):1669–74.
Xia Y, Hu X, Di K, Liu C, Tan T, Lin Y, Xu H, Xie H, Wang S, Yang Z, et al. Combined detection of exosome concentration and tumor markers in gastric cancer. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(2):252–8.
Zheng J, Huang X, Tan W, Yu D, Du Z, Chang J, Wei L, Han Y, Wang C, Che X, et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat Genet. 2016;48(7):747–57.
Meng LD, Shi GD, Ge WL, Huang XM, Chen Q, Yuan H, Wu PF, Lu YC, Shen P, Zhang YH, et al. Linc01232 promotes the metastasis of pancreatic cancer by suppressing the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of HNRNPA2B1 and activating the A-Raf-induced MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;494:107–20.
Shi J, Ma H, Wang H, Zhu W, Jiang S, Dou R, Yan B. Overexpression of LINC00261 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells progression by interacting with miR-522-3p and suppressing Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):18378–87.
Shahabi S, Kumaran V, Castillo J, Cong Z, Nandagopal G, Mullen DJ, Alvarado A, Correa MR, Saizan A, Goel R, et al. LINC00261 is an epigenetically regulated tumor suppressor essential for activation of the DNA damage response. Cancer Res. 2019;79(12):3050–62.
Yu Y, Li L, Zheng Z, Chen S, Chen E, Hu Y. Long non-coding RNA linc00261 suppresses gastric cancer progression via promoting Slug degradation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(5):955–67.
Fang Q, Sang L, Du S. Long noncoding RNA LINC00261 regulates endometrial carcinoma progression by modulating miRNA/FOXO1 expression. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018;36(6):323–30.
Wang X, Gao X, Tian J, Zhang R, Qiao Y, Hua X, Shi G. LINC00261 inhibits progression of pancreatic cancer by down-regulating miR-23a-3p. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;689:108469.
Zhang HF, Li W, Han YD. LINC00261 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and Notch signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018;21(3):575–82.
Lu K, Dong JL, Fan WJ. Twist1/2 activates MMP2 expression via binding to its promoter in colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(23):8210–9.
Murugan AK. mTOR: role in cancer, metastasis and drug resistance. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:92–111.
Zhou H, Huang S. mTOR signaling in cancer cell motility and tumor metastasis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2010;20(1):1–16.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81.
Dorn A, Glaß M, Neu CT, Heydel B, Hüttelmaier S, Gutschner T, Haemmerle M. LINC00261 is differentially expressed in pancreatic cancer subtypes and regulates a pro-epithelial cell identity. Cancers (Basel). 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051227.
Zhang B, Li C, Sun Z. Long non-coding RNA LINC00346, LINC00578, LINC00673, LINC00671, LINC00261, and SNHG9 are novel prognostic markers for pancreatic cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(8):2648–58.
Gonzalez DM, Medici D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal. 2014;7(344):re8.
Gurzu S, Kobori L, Fodor D, Jung I. Epithelial mesenchymal and endothelial mesenchymal transitions in hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:2962580.
Hu XT, Xing W, Zhao RS, Tan Y, Wu XF, Ao LQ, Li Z, Yao MW, Yuan M, Guo W, et al. HDAC2 inhibits EMT-mediated cancer metastasis by downregulating the long noncoding RNA H19 in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):270.
Gao Y, Zhang Z, Li K, Gong L, Yang Q, Huang X, Hong C, Ding M, Yang H. Linc-DYNC2H1–4 promotes EMT and CSC phenotypes by acting as a sponge of miR-145 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(7):e2924.
Hu Y, Zhang M, Tian N, Li D, Wu F, Hu P, Wang Z, Wang L, Hao W, Kang J, et al. The antibiotic clofoctol suppresses glioma stem cell proliferation by activating KLF13. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(8):3072–85.
Kwon SJ, Crespo-Barreto J, Zhang W, Wang T, Kim DS, Krensky A, Clayberger C. KLF13 cooperates with c-Maf to regulate IL-4 expression in CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2014;192(12):5703–9.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0902000); the fellowship of China postdoctoral science foundation (2020T130723); the Basic Scientific Research Business Expense Project of China Pharmaceutical University (No. 2632021ZD07); a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development (PADP) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BPL, SYP and YRZ initiated the study, and conceived and performed the experiments. JD contributed to the data analysis. CLZ and BYS contributed to the conception of the study and assisted with data interpretation. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Pang, S., Dou, J. et al. The inhibitory effect of LINC00261 upregulation on the pancreatic cancer EMT process is mediated by KLF13 via the mTOR signaling pathway. Clin Transl Oncol 24, 1059–1072 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02747-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02747-x