Abstract
Objectives
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is a consolidate treatment for inoperable early-stage lung tumors, usually delivered in single or multi-fraction regimens. We aimed to compare these two approaches in terms of local effectiveness, safety and survival.
Materials and methods
Patients affected by medically inoperable early-stage lung tumor were treated at two Institutions with two different schedules: 70 Gy in ten fractions (TF) (BED10: 119 Gy) or 30 Gy in single fraction (SF) (BED10: 120 Gy).
Results
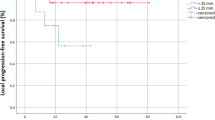
73 patients were treated with SBRT delivered with two biological equivalent schedules: SF (44) and TF (29). The median follow-up was 34 months (range 3–81 months). Three-year Overall survival (OS) was 57.9%, 3-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) was 77.2%, with no difference between treatment groups. Three-year progression-free survival (LPFS) was 88.9% and did not differs between SF and TF. Overall, four cases (5.4%) of acute grade ≥ 3 pneumonitis occurred. No differences in acute and late toxicity between the two groups were detected.
Conclusion
SF and TF seems to be equally safe and effective in the treatment of primary inoperable lung tumors especially for smaller lesion. The SF may be preferentially offered to reduce patient access to hospital with no negative impact on tumor control and survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi F, Arcangeli S, De Bari B, Giaj-Levra N, Fiorentino A, Mazzola R, Trovò M. Stage-I small cell lung cancer: A new potential option for stereotactic ablative radiation therapy? A review of literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;112:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.02.010.
Ball D, Mai GT, Vinod S, Babington S, Ruben J, Kron T, Chesson B, Herschtal A, Vanevski M, Rezo A, Elder C, Skala M, Wirth A, Wheeler G, Lim A, Shaw M, Schofield P, Irving L, Solomon B, TROG 09.02 CHISEL investigators. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard radiotherapy in stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer (TROG 09.02 CHISEL): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(4):494–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30896-9.
Nyman J, Hallqvist A, Lund JÅ, Brustugun OT, Bergman B, Bergström P, Friesland S, Lewensohn R, Holmberg E, Lax I. SPACE - A randomized study of SBRT vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy in medically inoperable stage I NSCLC. Radiother Oncol. 2016;121(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.08.015.
Nicosia L, Reverberi C, Agolli L, Marinelli L, De Sanctis V, Valeriani M, Osti MF. Long term results of single high dose Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the treatment of primary lung tumors. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15498. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51900-8.
Daly ME, Perks JR, Chen AM. Patterns-of-care for thoracic stereotactic body radiotherapy among practicing radiation oncologists in the United States. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:202–7.
Post CM, Verma V, Zhen W, Simone CB. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for 5 cm non-small cell lung cancer: survey of United States academic thoracic radiation oncologists. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;98:230–1.
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: Updated results of 257 patients in a japanese multi-institutional study. J Thoracic Oncol. 2007;2:S94-100.
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010;303:1070–6.
Haasbeek CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Slotman BJ, et al. Outcomes of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for centrally located early-stage lung cancer. J Thoracic Oncol. 2011;6:2036–43.
Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Shibata T, et al. Prospective trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for both operable and inoperable T1N0M0 non-small cell lung cancer: Japan clinical oncology group study JCOG0403. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:989–96.
Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(630–7):4.
Videtic GM, Paulus R, Singh AK, Chang JY, Parker W, Olivier KR, Timmerman RD, Komaki RR, Urbanic JJ, Stephans KL, Yom SS, Robinson CG, Belani CP, Iyengar P, Ajlouni MI, Gopaul DD, Gomez Suescun JB, McGarry RC, Choy H, Bradley JD. Long-term Follow-up on NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927): A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;103(5):1077–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.11.051.
Scorsetti M, Alongi F, Castiglioni S, Clivio A, Fogliata A, Lobefalo F, Mancosu P, Navarria P, Palumbo V, Pellegrini C, Pentimalli S, Reggiori G, Ascolese AM, Roggio A, Arcangeli S, Tozzi A, Vanetti E, Cozzi L. Feasibility and early clinical assessment of flattening filter free (FFF) based stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) treatments. Radiat Oncol. 2011;12(6):113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-6-113.
Mazzola R, Fersino S, Ferrera G, Targher G, Figlia V, Triggiani L, Pasinetti N, Lo Casto A, Ruggieri R, Magrini SM, Alongi F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung oligometastases impacts on systemic treatment-free survival: a cohort study. Med Oncol. 2018;35(9):121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1190-8.
Grimm J, LaCouture T, Croce R, Yeo I, Zhu Y, Xue J. Dose tolerance limits and dose volume histogram evaluation for stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2011;12(2):3368.
Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Mancosu P, Alongi F, Clerici E, Tozzi A, Iftode C, Reggiori G, Tomatis S, Infante M, Alloisio M, Testori A, Fogliata A, Cozzi L, Morenghi E, Scorsetti M. Volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free (FFF) beams for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with medically inoperable early stage non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Radiother Oncol. 2013;107(3):414–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.04.016.
Osti MF, Agolli L, Valeriani M, Reverberi C, Bracci S, Marinelli L, De Sanctis V, Cortesi E, Martelli M, De Dominicis C, Minniti G, Nicosia L. 30 Gy single dose stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): Report on outcome in a large series of patients with lung oligometastatic disease. Lung Cancer. 2018;122:165–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.06.018.
Mazzola R, Fiorentino A, Ricchetti F, Giaj Levra N, Fersino S, Di Paola G, Lo Casto A, Ruggieri R, Alongi F. Cone-beam computed tomography in lung stereotactic ablative radiation therapy: predictive parameters of early response. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1064):20160146. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20160146.
Quartuccio N, Evangelista L, Alongi P, Caobelli F, Altini C, Cistaro A, Lambertini A, Schiorlin I, Popescu CE, Linguanti F, Laudicella R, Scalorbi F, DiPierro G, Asabella AN, Cuppari L, Margotti S, Lima GM, Scalisi S, Pacella S, Kokomani A, Ciaccio A, Sturiale L, Vento A, Cardile D, Baldari S, Panareo S, Fanti S, Rubini G, Schillaci O, Chiaravalloti A, Young AIMN Working Group. Prognostic and diagnostic value of [18F]FDG-PET/CT in restaging patients with small cell lung carcinoma: an Italian multicenter study. Nucl Med Commun. 2019;40(8):808–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNM.0000000000001038.
Alongi P, Laudicella R, Gentile R, Scalisi S, Stefano A, Russo G, Grassedonio E, Albano D, Pompei G, Rossi F, Raimondo D, Ganduscio G, Midiri M, Sinagra E. Potential clinical value of quantitative fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/computed tomography using a graph-based method analysis in evaluation of incidental lesions of gastrointestinal tract: correlation with endoscopic and histopathological findings. Nucl Med Commun. 2019;40(10):1060–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNM.0000000000001062.
Eisenhauer E, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Pinker K, Riedl C, Weber WA. Evaluating tumor response with FDG PET: updates on PERCIST, comparison with EORTC criteria and clues to future developments. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2017;44(Suppl 1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3687-3.
Mazzola R, Ruggieri R, Figlia V, Rigo M, Giaj Levra N, Ricchetti F, Nicosia L, Corradini S, Alongi F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy of central lung malignancies using a simultaneous integrated protection approach : A prospective observational study. Strahlenther Onkol. 2019;195(8):719–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-018-01419-0.
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, Fakiris A, Bezjak A, Videtic G, Johnstone D, Fowler J, Gore E, Choy H. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010;303(11):1070–6. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.261.
Adebahr S, Collette S, Shash E, Lambrecht M, Le Pechoux C, Faivre-Finn C, De Ruysscher D, Peulen H, Belderbos J, Dziadziuszko R, Fink C, Guckenberger M, Hurkmans C, Nestle U. LungTech, an EORTC Phase II trial of stereotactic body radiotherapy for centrally located lung tumours: a clinical perspective. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1051):20150036. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20150036.
Navarro-Martin A, Aso S, Cacicedo J, Arnaiz M, Navarro V, Rosales S, de Blas R, Ramos R, Guedea F. Phase II Trial of SBRT for Stage I NSCLC: Survival, Local Control, and Lung Function at 36 Months. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(7):1101–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.021.
Timmerman RD, Paulus R, Pass HI, Gore EM, Edelman MJ, Galvin J, Straube WL, Nedzi LA, McGarry RC, Robinson CG, Schiff PB, Chang G, Loo BW Jr, Bradley JD, Choy H. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for operable early-stage lung cancer: findings from the NRG oncology RTOG 0618 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(9):1263–6. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1251.
Ma SJ, Serra LM, Syed YA, Hermann GM, Gomez-Suescun JA, Singh AK. Comparison of single- and three-fraction schedules of stereotactic body radiation therapy for peripheral early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(2):e235–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2017.10.010 (Epub 2017 Oct 28).
Cummings MA, Ma SJ, Hermann G, Serra L, Syed Y, Malhotra HK, Chen Y, Milano MT, Gomez-Suescun JA, Singh DP, Singh AK. Comparison of single- and five-fraction regimens of stereotactic body radiation therapy for peripheral early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: a two-institution propensity-matched analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2018.07.006.
Borghetti P, Bonù ML, Roca E, Pedretti S, Salah E, Baiguini A, Greco D, Triggiani L, Maddalo M, Levra NG, Alongi F, Magrini SM, Buglione M. Radiotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: real-life experience. Vivo. 2018;32(1):159–64.
Guckenberger M, Andratschke N, Dieckmann K, Hoogeman MS, Hoyer M, Hurkmans C, Tanadini-Lang S, Lartigau E, Méndez Romero A, Senan S, Verellen D. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on implementation and practice of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2017;124(1):11–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2017.05.012.
Rothkamm K, Kruger I, Thompson LH, et al. Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair duringthe mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:5706–15.
Carlson DJ, Keall PJ, Loo BW Jr, et al. Hypofractionation results in reduced tumor cell kill compared to conventional fractionation for tumors with regions of hypoxia. Int J Radiat OncolBiol Phys. 2011;79:1188–95.
Brown JM, Diehn M, Loo BW Jr. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy should be combined with a hypoxic cell radiosensitizer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78:323–7.
Shuryak I, Carlson DJ, Brown JM, Brenner DJ. High-dose and fractionation effects in stereotactic radiation therapy: Analysis of tumor control data from 2965 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2015;115(3):327–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2015.05.013.
Milano MT, Zhang H, Usuki KY, Singh DP, Chen Y. Definitive radiotherapy for stage I non small cell lung cancer: a population-based study of survival. Cancer. 2012;118:5572–9.
Beitler JJ, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for nonmetastatic lung cancer: an analysis of 75 patients treated over 5 years. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65:100–6.
Kim MS, Kim W, Park IH, Kim HJ, Lee E, Jung JH, Cho LC, Song CW. Radiobiological mechanisms of stereotactic body radiation therapy and stereotactic radiation surgery. Radiat Oncol J. 2015;33(4):265–75. https://doi.org/10.3857/roj.2015.33.4.265.
Ruggieri R, Stavrev P, Naccarato S, Stavreva N, Alongi F, Nahum AE. Optimal dose and fraction number in SBRT of lung tumours: A radiobiological analysis. Phys Med. 2017;44:188–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2016.12.012.
Shibamoto Y, Hashizume C, Baba F, Ayakawa S, Miyakawa A, Murai T, Takaoka T, Hattori Y, Asai R. Stereotactic body radiotherapy using a radiobiology-based regimen for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: five-year mature results. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(6):960–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000525.
Yamada Y, Katsoulakis E, Laufer I, Lovelock M, Barzilai O, McLaughlin LA, Zhang Z, Schmitt AM, Higginson DS, Lis E, Zelefsky MJ, Mechalakos J, Bilsky MH. The impact of histology and delivered dose on local control of spinal metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42(1):E6. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.FOCUS16369.
Folkert MR, Timmerman RD. Stereotactic ablative body radiosurgery (SABR) or Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;15(109):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.11.005.
Ng SSW, Ning MS, Lee P, McMahon RA, Siva S, Chuong MD. Single-fraction stereotactic body radiation therapy: a paradigm during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and beyond? Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020;5(4):761–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2020.06.011.
Singh AK, Gomez-Suescun JA, Stephans KL, Bogart JA, Hermann GM, Tian L, Groman A, Videtic GM. One versus three fractions of stereotactic body radiation therapy for peripheral stage I to II non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized, multi-institution, phase 2 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;105(4):752–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.08.019.
Videtic GM, Stephans KL, Woody NM, Reddy CA, Zhuang T, Magnelli A, Djemil T. 30 Gy or 34 Gy? Comparing 2 single-fraction SBRT dose schedules for stage I medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90(1):203–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.05.017.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Original research concept and final revision of the manuscript: L.N. F.A., M.F.O.; writing contribution: R.M. N.G.L.; literature search: V.F.; data collection: V.F., C.R.; data storage: V.D.S.; statistical analysis: L.N. M.V.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
Filippo Alongi, Luca Nicosia, Vanessa Figlia, Vitaliana De Sanctis, Rosario Mazzola, Niccolò Giaj-Levra, Chiara Reverberi, Maurizio Valeriani, Mattia F. Osti declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alongi, F., Nicosia, L., Figlia, V. et al. A multi-institutional analysis of fractionated versus single-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in the treatment of primary lung tumors: a comparison between two antipodal fractionations. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 2133–2140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02619-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02619-4