Abstract
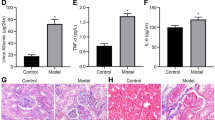
The current study was designed to explore the potential involvement of miR-155 in the pathogenesis of diabetes complications. Male rats were divided into control and diabetic groups (n = 6). Type 2 diabetes was induced by a single-dose injection of nicotinamide (110 mg/kg; intraperitoneal (i.p.)), 15 min before injection of streptozotocin (STZ; 50 mg/kg; i.p.) in 12-h fasted rats. Two months after induction of diabetes, the rats were sacrificed for subsequent measurements. The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity was higher in diabetic peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), aorta, heart, kidney, liver, and sciatic nerve, than the control counterparts. Also, apoptosis rate was increased in these tissues, except the aorta. NF-κB messenger RNA (mRNA) expression level was higher in the kidney, heart, PBMCs, and sciatic nerve of diabetic rats than their control counterparts. Except the liver, the miR-155 expression level was significantly decreased in diabetic kidney, heart, aorta, PBMCs, and sciatic nerve versus the controls. Moreover, the expression of miR-155 was negatively correlated with NF-κB activity and apoptosis rate. These results suggest that changes in the expression of miR-155 may participate in the pathogenesis of diabetes-related complications, but causal relationship between miR-155 dysregulation and diabetic complications is unknown.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alipour MR, Khamaneh AM, Yousefzadeh N, Mohammad-nejad D, Soufi FG (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-146a was not accompanied by downregulation of pro-inflammatory markers in diabetic kidney. Mol Biol Rep 40:6477–6483
Bala S, Marcos M, Kodys K, Csak T, Catalano D, Mandrekar P, Szabo G (2011) Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J Biol Chem 286:1436–1444
Brasier AR (2006) The NF-kappaB regulatory network. Cardiovasc Toxicol 6:111–130
Corral-Fernández NE, Salgado-Bustamante M, Martínez-Leija ME, Cortez-Espinosa N, García-Hernández MH, Reynaga-Hernández E, Quezada-Calvillo R, Portales-Pérez DP (2013) Dysregulated miR-155 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 121:347–353
Cremer TJ, Fatehchand K, Shah P, Gillette D, Patel H, Marsh RL, Besecker BY, Rajaram MV, Cormet-Boyaka E, Kanneganti TD, Schlesinger LS, Butchar JP, Tridandapani S (2012) MiR-155 induction by microbes/microbial ligands requires NF-κB-dependent de novo protein synthesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:73
Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J, Bonmassar E (2009) MiR-155 gene: a typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:497–505
Fink T, Lund P, Pilgaard L, Rasmussen JG, Duroux M, Zachar V (2008) Instability of standard PCR reference genes in adipose-derived stem cells during propagation, differentiation and hypoxic exposure. BMC Mol Biol 9:98
Guay C, Roggli E, Nesca V, Jacovetti C, Regazzi R (2011) Diabetes mellitus, a microRNA-related disease? Transl Res 157:253–264
Imaizumi T, Tanaka H, Tajima A, Yokono Y, Matsumiya T, Yoshida H, Tsuruga K, Aizawa-Yashiro T, Hayakari R, Inoue I, Ito E, Satoh K (2010) IFN-γ and TNF-α synergistically induce microRNA-155 which regulates TAB2/IP-10 expression in human mesangial cells. Am J Nephrol 32:462–468
King GL (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetes and its complications. J Periodontol 79(8 Suppl):1527–1534
Ma X, Becker Buscaglia LE, Barker JR, Li Y (2011) MicroRNAs in NF-kappaB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol 3:159–166
Palomer X, Capdevila-Busquets E, Alvarez-Guardia D, Barroso E, Pallàs M, Camins A, Davidson MM, Planavila A, Villarroya F, Vázquez-Carrera M (2013) Resveratrol induces nuclear factor-κB activity in human cardiac cells. Int J Cardiol 167:2507–2516
Patel S, Santani D (2009) Role of NF-kappa B in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications. Pharmacol Rep 61:595–603
Peltier HJ, Latham GJ (2008) Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 14:844–852
Pitocco D, Tesauro M, Alessandro R, Ghirlanda G, Cardillo C (2013) Oxidative stress in diabetes: implications for vascular and other complications. Int J Mol Sci 14:21525–21550
Rains JL, Jain SK (2011) Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med 50:567–575
Raisch J, Darfeuille-Michaud A, Nguyen HT (2013) Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J Gastroenterol 19:2985–2996
Roghani M, Baluchnejadmojarad T (2010) Mechanisms underlying vascular effect of chronic resveratrol in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Phytother Res 24:S148–S154
Rydén L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Berne C, Cosentino F et al (2013) ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 34:3035–3087
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM, Moreno JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A (2010) NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1254–1262
Singh CK, Kumar A, Hitchcock DB, Fan D, Goodwin R, LaVoie HA, Nagarkatti P, DiPette DJ, Singh US (2011) Resveratrol prevents embryonic oxidative stress and apoptosis associated with diabetic embryopathy and improves glucose and lipid profile of diabetic dam. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:1186–1196
Soufi FG, Sheervalilou R, Vardiani M, Khalili M, Alipour MR (2012) Chronic resveratrol administration has beneficial effects in experimental model of type 2 diabetic rats. Endocr Regul 46:83–90
Soufi FG, Vardyani M, Sheervalilou R, Mohammadi M, Somi MH (2012) Long-term treatment with resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress pro-inflammatory mediators and apoptosis in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Gen Physiol Biophys 31:431–438
Spinetti G, Cordella D, Fortunato O, Sangalli E, Losa S, Gotti A, Carnelli F, Rosa F, Riboldi S, Sessa F, Avolio E, Beltrami AP, Emanueli C, Madeddu P (2013) Global remodeling of the vascular stem cell niche in bone marrow of diabetic patients: implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Circ Res 112:510–522
Thompson RC, Herscovitch M, Zhao I, Ford TJ, Gilmore TD (2011) NF-kappaB down-regulates expression of the B-lymphoma marker CD10 through a miR-155/PU.1 pathway. J Biol Chem 286:1675–1682
Villeneuve LM, Reddy MA, Natarajan R (2011) Epigenetics: deciphering its role in diabetes and its chronic complications. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38:451–459
Wang B, Majumder S, Nuovo G, Kutay H, Volinia S, Patel T, Schmittgen TD, Croce C, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST (2009) Role of microRNA-155 at early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by choline-deficient and amino acid-defined diet in C57BL/6 mice. Hepatology 50:1152–1161
Xiao B, Liu Z, Li BS, Tang B, Li W, Guo G, Shi Y, Wang F, Wu Y, Tong WD, Guo H, Mao XH, Zou QM (2009) Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J Infect Dis 200:916–925
Zhou X, Wang B, Zhu L, Hao S (2012) A novel improved therapy strategy for diabetic nephropathy: targeting AGEs. Organogenesis 1:18–21
Acknowledgments
The grant of this study was supported by Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure 2
Hematoxylin and Eosin histopatholgical micrograph of the liver from normal (A1 and A2) and diabetic (B1 and B2) rats, 2 months after induction of diabetes. Arrows indicate polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration and typical cholangitis. Original magnification: × 40. Scale bar, 1 mm (TIFF 4341 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khamaneh, A.M., Alipour, M.R., Sheikhzadeh Hesari, F. et al. A signature of microRNA-155 in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. J Physiol Biochem 71, 301–309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0413-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0413-0