Abstract
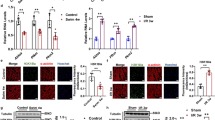
The blood O2-carrying capacity is maintained by the O2-regulated production of erythropoietin (Epo), which stimulates the proliferation and survival of red blood cell progenitors. Epo has been thought to act exclusively on erythroid progenitor cells. However, recent studies have identified the erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) in other cells, such as neurons, astrocytes, microglia, heart, cancer cell lines, and skeletal muscle provides evidence for a potential role of Epo in other tissues. In this study we aimed to determine the effect of recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEpo) on skeletal muscle adaptations such as mitochondrial biogenesis, myogenesis, and angiogenesis in different muscle fibre types. Fourteen male Wistar rats were randomly divided into two experimental groups, and saline or rHuEpo (300 IU) was administered subcutaneously three times a week for 3 weeks. We evaluated the protein expression of intermediates involved in the mitochondrial biogenesis cascade, the myogenic cascade, and in angiogenesis in the oxidative soleus muscle and in the glycolytic gastrocnemius muscle. Contrary to our expectations, rHuEpo significantly hampered the mitochondrial biogenesis pathway in gastrocnemius muscle (PGC-1α, mTFA and cytochrome c). We did not find any effect of the treatment on cellular signals of myogenesis (MyoD and Myf5) or angiogenesis (VEGF) in either soleus or gastrocnemius muscles. Finally, we found no significant effect on the maximal aerobic velocity at the end of the experiment in the rHuEpo-treated animals. Our findings suggest that 3 weeks of rHuEpo treatment, which generates an increase of oxygen carrying capacity, can affect mitochondrial biogenesis in a muscle fibre-specific dependent manner.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acs G, Acs P, Beckwith SM, Pitts RL, Clements E, Wong K, Verma A (2001) Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor expression in human cancer. Cancer Res 61:3561–3565
Brooks GA, White TP (1978) Determination of metabolic and heart rate responses of rats to treadmill exercise. J Appl Physiol 45:1009–1015
Carlini RG, Reyes AA, Rothstein M (1995) Recombinant human erythropoietin stimulates angiogenesis in vitro. Kidney Int 47:740–745
Carraway MS, Suliman HB, Jones WS, Chen CW, Babiker A, Piantadosi CA (2010) Erythropoietin activates mitochondrial biogenesis and couples red cell mass to mitochondrial mass in the heart. Circ Res 106:1722–1730
Cayla J, Lavoie C, Gareau R, Duvallet A (1999) Effects of recombinant erythropoietin (r-HuEPO) on plasma glucose concentration in endurance-trained rats. Acta Physiol Scand 166:247–249
Cayla JL, Maire P, Duvallet A, Wahrmann JP (2008) Erythropoietin induces a shift of muscle phenotype from fast glycolytic to slow oxidative. Int J Sports Med 29:460–465
Davies KJ, Packer L, Brooks GA (1982) Exercise bioenergetics following sprint training. Arch Biochem Biophys 215:260–265
Digicaylioglu M, Bichet S, Marti HH, Wenger RH, Rivas LA, Bauer C, Gassmann M (1995) Localization of specific erythropoietin binding sites in defined areas of the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3717–3720
Dumont M, Stack C, Elipenahli C, Jainuddin S, Gerges M, Starkova NN, Yang L, Starkov AA, Beal F (2011) Behavioral deficit, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction precede tau pathology in P301S transgenic mice. FASEB J 25:4063–4072
Foskett A, Alnaeeli M, Wang L, Teng R, Noguchi CT (2011) The effects of erythropoietin dose titration during high-fat diet-induced obesity. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:373781
Gamboa JL, Andrade FH (2010) Mitochondrial content and distribution changes specific to mouse diaphragm after chronic normobaric hypoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R575–R583
Gomez-Cabrera MC, Domenech E, Romagnoli M, Arduini A, Borras C, Pallardo FV, Sastre J, Viña J (2008) Oral administration of vitamin C decreases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and hampers training-induced adaptations in endurance performance. Am J Clin Nutr 87:142–149
Gore CJ, Clark SA, Saunders PU (2007) Nonhematological mechanisms of improved sea-level performance after hypoxic exposure. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1600–1609
Hojman P, Brolin C, Gissel H, Brandt C, Zerahn B, Pedersen BK, Gehl J (2009) Erythropoietin over-expression protects against diet-induced obesity in mice through increased fat oxidation in muscles. PLoS One 4:e5894
Holloszy JO (1967) Biochemical adaptations in muscle. Effects of exercise on mitochondrial oxygen uptake and respiratory enzyme activity in skeletal muscle J Biol Chem 242:2278–2282
Hood DA (2001) Invited review: contractile activity-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 90:1137–1157
Hoppeler H, Vogt M (2001) Muscle tissue adaptations to hypoxia. J Exp Biol 204:3133–3139
Jelkmann W (1986) Erythropoietin research, 80 years after the initial studies by Carnot and Deflandre. Respir Physiol 63:257–266
Juel C, Thomsen JJ, Rentsch RL, Lundby C (2007) Effects of prolonged recombinant human erythropoietin administration on muscle membrane transport systems and metabolic marker enzymes. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:41–44
Leick L, Lyngby SS, Wojtasewski JF, Pilegaard H (2010) PGC-1alpha is required for training-induced prevention of age-associated decline in mitochondrial enzymes in mouse skeletal muscle. Exp Gerontol 45:336–342
Levett DZ, Radford EJ, Menassa DA, Graber EF, Morash AJ, Hoppeler H, Clarke K, Martin DS, Ferguson-Smith AC, Montgomery HE, Grocott MP, Murray AJ (2011) Acclimatization of skeletal muscle mitochondria to high-altitude hypoxia during an ascent of Everest. FASEB J. doi:10.1096/fj.11-197772
Lundby C, Hellsten Y, Jensen MB, Munch AS, Pilegaard H (2008) Erythropoietin receptor in human skeletal muscle and the effects of acute and long-term injections with recombinant human erythropoietin on the skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 104:1154–1160
Lundby C, Olsen NV (2011) Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in normal humans. J Physiol 589:1265–1271
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Miyake M, Hayashi S, Sato T, Taketa Y, Watanabe K, Tanaka S, Ohwada S, Aso H, Yamaguchi T (2007) Myostatin and MyoD family expression in skeletal muscle of IGF-1 knockout mice. Cell Biol Int 31:1274–1279
Norrbom J, Sundberg CJ, Ameln H, Kraus WE, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2004) PGC-1α mRNA expression is influenced by metabolic perturbation in exercising human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 96:189–194
Ogilvie M, Yu X, Nicolas-Metral V, Pulido SM, Liu C, Ruegg UT, Noguchi CT (2000) Erythropoietin stimulates proliferation and interferes with differentiation of myoblasts. J Biol Chem 275:39754–39761
Pilegaard H, Saltin B, Neufer PD (2000) Exercise induces transient transcriptional activation of the PGC-1 gene in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 546:851–858
Pownall ME, Gustafsson MK, Emerson CP Jr (2002) Myogenic regulatory factors and the specification of muscle progenitors in vertebrate embryos. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:747–783
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM (1998) A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 92:829–839
Rotter R, Menshykova M, Winkler T, Matziolis G, Stratos I, Schoen M, Bittorf T, Mittlmeier T, Vollmar B (2008) Erythropoietin improves functional and histological recovery of traumatized skeletal muscle tissue. J Orthop Res 26:1618–1626
Rundqvist H, Rullman E, Sundberg CJ, Fischer H, Eisleitner K, Stahlberg M, Sundblad P, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2009) Activation of the erythropoietin receptor in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Endocrinol 161:427–434
Sanchis-Gomar F, Martinez-Bello VE, Domenech E, Nascimento AL, Pallardo FV, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Viña J (2009) Effect of intermittent hypoxia on hematological parameters after recombinant human erythropoietin administration. Eur J Appl Physiol 107:429–436
Scoppetta C, Grassi F (2004) Erythropoietin: a new tool for muscle disorders? Med Hypotheses 63:73–75
Sinclair AM, Coxon A, McCaffery I, Kaufman S, Paweletz K, Liu L, Busse L, Swift S, Elliott S, Begley CG (2010) Functional erythropoietin receptor is undetectable in endothelial, cardiac, neuronal, and renal cells. Blood 115:4264–4272
Verbrugge DJ, Goodnough LT (1994) The effect of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment on the endurance performance of Sprague–Dawley rats. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 54:55–59
Virbasius JV, Scarpulla RC (1994) Activation of the human mitochondrial transcription factor A gene by nuclear respiratory factors: a potential regulatory link between nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression in organelle biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:1309–1313
Wang L, Chopp M, Gregg SR, Zhang RL, Teng H, Jiang A, Feng Y, Zhang ZG (2008) Neural progenitor cells treated with EPO induce angiogenesis through the production of VEGF. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1361–1368
Wu H, Lee SH, Gao J, Liu X, Iruela-Arispe ML (1999) Inactivation of erythropoietin leads to defects in cardiac morphogenesis. Development 126:3597–3605
Wu Z, Puigserver P, Andersson U, Zhang C, Adelmant G, Mootha V, Troy A, Cinti S, Lowell B, Scarpulla RC, Spiegelman BM (1999) Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98:115–124
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants SAF2009-08334; SAF2010-19498 from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (MEC); ISCIII2006-RED13-027 from the “Red Temática de investigación cooperativa en envejecimiento y fragilidad (RETICEF); PROMETEO2010/074, and EU Funded COSTB35. This study was co-financed by FEDER funds from the European Union. Martínez-Bello VE received of a research fellowship from the Research and Scientific Policy Department of the University of Valencia, Spain, and EPICA (Empresa de Productos de Investigación y Ciencias Aplicadas, Spain). Sanchis-Gomar received of a research fellowship from the Conselleria d’ Educació, Generalitat Valenciana, “VALi + d program”. We thank Mrs. Marilyn Noyes for her kind help in reviewing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors had any conflicts of interest with the funding agencies or professional relationships with companies or manufacturers who may benefit from the results of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez-Bello, V.E., Sanchis-Gomar, F., Romagnoli, M. et al. Three weeks of erythropoietin treatment hampers skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in rats. J Physiol Biochem 68, 593–601 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0178-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0178-7