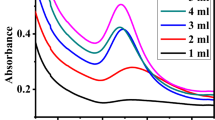
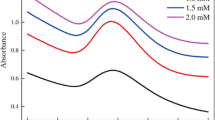
Abstract
The environmental pollution caused by chemical dyes is a growing concern nowadays. Limitations of traditional methods opened the route for nanotechnology; owing to the versatile properties of nanomaterials, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) became a potential strategy for different applications. In the present study, biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (BioAuNPs) was carried out by reacting chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) with cell-free filtrate of Penicillium rubens sp. nov. NCIM 1937. The AuNPs were then characterized by UV–visible spectroscopy, HR-TEM, FTIR, and DLS analysis to further examine their efficacious biosynthesis and morphological properties including size, shape, and stability. The biogenic AuNPs are polydisperse in nature, with a mean size of 14.92 ± 5 nm. These AuNPs exhibited promising antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli NCIM-2065, Bacillus subtilis NCIM-2010, and Penicillium verrucosum MTCC 4935. In vitro quantitative HPLC results revealed that BioAuNPs significantly inhibited the biosynthesis of ochratoxin A (OTA). Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are intriguing for power generation and wastewater treatment since they can directly transform chemical energy stored in organic matter to electricity by extracellular electron transfer (EET) via membrane proteins. AuNPs also showed excellent potential for dye degradation of organic pollutants, viz., methylene blue (MB), phenol red (PR), bromothymol blue (BTB), Congo red (CR), and 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). All dye removal efficiencies were estimated and fitted to pseudo-first-order processes using kinetic rate constants (Ka).The present study reveals a simple, original, and eco-friendly method for the synthesis of multifunctional biogenic AuNPs that could be effective in OTA detoxification in food products and organic pollutant removal during wastewater treatment for a sustainable environment.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Kareem MM, Zohri AA (2018) Extracellular mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Trichoderma hamatum: optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J Appl Microbiol 67(5):465–475. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13055
Abdi M, Asadi A, Maleki F, Kouhsari E, Fattahi A, Ohadi E, Lotfali E, Ahmadi A, Ghafouri Z (2021) Microbiological detoxification of mycotoxins: focus on mechanisms and advances. Infect Disord Drug Targets 21(3):339–357. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871526520666200616145150
Aboelghar M, Wahab HA (2013) Spectral footprint of Botrytis cinerea, a novel way for fungal characterization. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 04(03):374–382. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2013.43050
Abu-Tahon MA, Ghareib M, Abdallah WE (2020) Environmentally benign rapid biosynthesis of extracellular gold nanoparticles using Aspergillus flavus and their cytotoxic and catalytic activities. Process Biochem 95:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.04.015
Al-Asfar A, Zaheer Z, Aazam ES (2018) Eco-friendly green synthesis of Ag@Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: antioxidant, antimicrobial and photocatalytic degradation of bromothymol blue. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 185:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.05.028
Al-Thabaiti SA, Khan Z (2020) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles, sensing and photo catalytic activities for bromothymol blue. J Photochem Photobiol A 3–4:100010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpap.2020.100010
Barabadi H, Honary S, Ebrahimi P, Mohammadi MA, Alizadeh A, Naghibi F (2014) Microbial mediated preparation, characterization and optimization of gold nanoparticles. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1493–1501. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822014000400046
Bhargava A, Jain N, Khan MA, Pareek V, Dilip RV, Panwar J (2016) Utilizing metal tolerance potential of soil fungus for efficient synthesis of gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic activity for degradation of rhodamine B. J Environ Manag 183:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.021
Biswal AK, Misra PK (2020) Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles for prospective application in food packaging and biomedical fields. Mater Chem Phys 250:123014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123014
Bui-Klimke TR, Wu F (2015) Ochratoxin A and human health risk: a review of the evidence. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 55(13):1860–1869. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2012.724480
Cao B, Zhao Z, Peng L, Shiu HY, Ding M, Song F, Guan X, Lee CK, Huang J, Zhu D, Fu X, Wong GCL, Liu C, Nealson K, Weiss PS, Duan X, Huang Y (2021). Silver nanoparticles boost charge-extraction efficiency in Shewanella microbial fuel cells. Sci 17;373(6561):1336–1340. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf3427
Chen CY, Chang YC, Tsai TH, Liu MH, Chung YC (2021) Multifunctional activities of gold nanoparticles biosynthesized using bacteria isolated from mining areas. Appl Sci 11(8):3670. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083670
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2014) Green synthesis of protein capped silver nanoparticles from phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina Goid with antimicrobial properties against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:365. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-365
Clarance P, Luvankar B, Sales J, Khusro A, Agastian P, Tack JC, Al Khulaifi MM, AL-Shwaiman HA, Elgorban AM, Syed A, Kim HJ (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using endophytic fungi Fusarium solani and its in-vitro anticancer and biomedical applications. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(2):706–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.026
Du C, He S, Gao X, Chen W (2016) Hierarchical Cu@MnO2 core-shell nanowires: a nonprecious-metal catalyst with an excellent catalytic activity toward the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. ChemCatChem 8(18):2885–2889. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201600567
Du Liangwei, Qiuhong Xu, Meiying H, Liang X, Jia-Xun F (2015) Synthesis of small silver nanoparticles under light radiation by fungus Penicillium oxalicum and its application for the catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Materials Chemistry and Physics 160:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.04.003
Fernando I, Zhou Y (2019) Impact of pH on the stability, dissolution and aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 216:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.122
Fothergill AW (2011) Antifungal susceptibility testing: Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute (CLSI) methods. Interact Yeasts, Moulds, Antifungal Agents 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-134-5_2
Fouda A, Hassan SED, Eid AM, Abdel‐Rahman MA, Hamza MF (2022) Light enhanced the antimicrobial, anticancer, and catalytic activities of selenium nanoparticles fabricated by endophytic fungal strain, Penicillium crustosum EP-1. Sci Rep 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15903-2
Fulya G, Ayşenur A, Mehmet G, Sadin O, Serpil G, Fatih Ş (2021) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and investigation of antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and DNA cleavage activities. Appl Organomet Chem e6272. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6272
Ganapuram BR, Alle M, Dadigala R, Dasari A, Maragoni V, Guttena V (2015) Catalytic reduction of methylene blue and Congo red dyes using green synthesized gold nanoparticles capped by Salmalia malabarica gum. Int Nano Lett 5(4):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-015-0158-3
Gibson NM, Luo TJM, Brenner DW, Shenderova O (2011) Immobilization of mycotoxins on modified nanodiamond substrates. Biointerphases 6:210– 217. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.3672489
Göl F, Aygün A, Seyrankaya A, Gür T, Yenikaya C, Şen F (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of Camellia sinensis mediated silver nanoparticles for antibacterial ceramic applications. Mater Chem Phys 250:123037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123037
Gulati S, Sachdeva M, Bhasin KK (2018) Capping agents in nanoparticle synthesis: surfactant and solvent system. AIP Conf Proc 1953:030214. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032549
Gulbagca F, Ozdemir S, Gulcan M, Sen F (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Rosa canina-mediated biogenic silver nanoparticles for anti-oxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and DNA cleavage activities. Heliyon 5(12):e02980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02980
Gulbagca F, Aygün A, Gülcan M, Ozdemir S, Gonca S, Şen F (2021) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: preparation, characterization, and investigation of antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and DNA cleavage activities. Appl Organomet Chem e6272. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6272
Gur T, Meydan I, Seckin H, Bekmezci M, Sen F (2022) Green synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ Res 204:111897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111897
Horky P, Skalickova S, Baholet D, Skladanka J (2018) Nanoparticles as a solution for eliminating the risk of mycotoxins. Nanomaterials 8(9):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090727
Houbraken J, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2011) Fleming’s penicillin producing strain is not Penicillium chrysogenum but P. rubens. IMA Fungus 2(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.5598/imafungus.2011.02.01.12
IARC (1993) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, some naturally occurring substances: food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins, in IARC Science Publications (Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer). 489–521
Khan MN, Bashir O, Khan TA, AL-Thabaiti SA, Khan Z (2018) CTAB capped synthesis of bio-conjugated silver nanoparticles and their enhanced catalytic activities. J Mol Liq 258:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.130
Kim B, Song WC, Park SY, Park G (2021) Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles via Sargassum serratifolium extract for catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Catalysts 11(3):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030347
Koteswara Rao V, Girisham S (2014) Antimicrobial and DNA damaging activity of ochratoxin a extracted from Penicillium Species. Int J Phar Biosci 5(4):335–341
Koteswara Rao V, Girisham S, Madhusudhan Reddy S (2016) Prevalence of toxigenic Penicillium species associated with poultry house in Telangana. India Arch Environ Occup Health 71(6):353–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/19338244.2016.1140627
Kotzybik K, Gräf V, Kugler L, Stoll DA, Greiner R, Geisen R, Schmidt-Heydt M (2016) Influence of different nanomaterials on growth and mycotoxin production of Penicillium verrucosum. PLOS One 11(3):e0150855. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150855
Kumar I, Mondal M, Meyappan V, Sakthivel N (2019) Green one-pot synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Sansevieria roxburghiana leaf extract for the catalytic degradation of toxic organic pollutants. Mater Res Bull 117:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.04.029
Kumari P, Meena A (2020) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Lawsonia inermis and its catalytic activities following the Langmuir-Hinshelwood mechanism. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 606:125447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.12544
Lin J, Gulbagca F, Aygun A, Elhouda Tiri RN, Xia C, Van Le Q, Gur T, Sen F, Vasseghian Y (2022) Phyto-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications on hydrogen generation on NaBH4, biological activities and photodegradation on azo dyes: development of machine learning model. Food Chem Toxicol: an Int J Published Br Ind Biol Res Assoc 163:112972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112972
López-Lorente ÁI, Cárdenas S, González-Sánchez ZI (2019) Effect of synthesis, purification and growth determination methods on the antibacterial and antifungal activity of gold nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 103:109805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109805
Lotfali E, Toreyhi H, Makhdoomi Sharabiani K, Fattahi A, Soheili A, Ghasemi R, Keymaram M, Rezaee Y, Iranpanah S (2020) Comparison of antifungal properties of gold, silver, and selenium nanoparticles against amphotericin B-resistant Candida glabrata clinical isolates. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.18502/ajmb.v13i1.4578
Mehmood S, Janjua NK, Saira F, Fenniri H (2016) AuCu@Pt nanoalloys for catalytic application in reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Spectrosc 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6210794
Mishra A, Kumari M, Pandey S, Chaudhry V, Gupta KC, Nautiyal CS (2014) Biocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of gold nanoparticles synthesized by Trichoderma sp. Bioresour Technol 166:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.085
Molnár Z, Bódai V, Szakacs G, Erdélyi B, Fogarassy Z, Sáfrán G, Varga T, Kónya Z, Tóth-Szeles E, Szűcs R, Lagzi I (2018) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by thermophilic filamentous fungi. Sci Rep 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22112-3
Navale V, Vamkudoth KR, Ajmera S, Dhuri V (2021) Aspergillus derived mycotoxins in food and the environment: prevalence, detection, and toxicity. Toxicol Rep 8:1008–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.04.013
Ovais M, Khalil AT, Raza A, Islam NU, Ayaz M, Saravanan M, Ali M, Ahmad I, Shahid M, Shinwari ZK (2018) Multifunctional theranostic applications of biocompatible green-synthesized colloidal nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(10):4393–4408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8928-2
Pei X, Qu Y, Shen W, Li H, Zhang X, Li S, Zhang Z, Li X (2017) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using fungus Mariannaea sp. HJ and their catalysis in reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(27):21649–21659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9684-z
Philip H (2017) Handbook of environmental fate and exposure data. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203719305
Portal González N, Soler A, Ribadeneira C, Solano J, Portieles R, Herrera Isla L, Companioni B, Borras-Hidalgo O, Santos Bermudez R (2021) Phytotoxic metabolites produce by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense Race 2. Front Microbiol 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.629395
Prante M, Segal E, Scheper T, Bahnemann J, Walter J (2020) Aptasensors for point-of-care detection of small molecules. Biosensors 10(9):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10090108
Puzyr AP, Purtov KV, Shenderova OA, Luo M, Brenner DW, Bondar VS (2007) The adsorption of aflatoxin B1 by detonation-synthesis nanodiamonds. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys 417:299–301. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672907060026
Qu Y, Li X, Lian S, Dai C, Jv Z, Zhao B, Zhou H (2018) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using fungus Trichoderma sp. WL‐Go and their catalysis in degradation of aromatic pollutants. IET Nanobiotechnol 13(1):12–17. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5177
Radini IA, Hasan N, Malik MA, Khan Z (2018) Biosynthesis of iron nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract for photocatalytic methyl orange dye degradation and antibacterial applications. J Photochem Photobiol B 183:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.014
Radhakrishnan R, Uthirappan M, Arumugam G, Muthiah S (2021) Myco-Fabricated Gold Nanoparticles from Aspergillus tamarii MTCC5152, its Characterization and Dye Biodegradation. Appl Microbiol Theory Technol 2(2):52–56. https://doi.org/10.37256/amtt.222021792
Rajasekar T, Karthik K, Muralitharan G, Maryshamya A, Sabarika S, Anbarasu S, Revathy K, Prasannabalaji N, Kumaran S (2020) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using extracellular metabolites of fish gut microbes and their antimicrobial properties. Braz J Microbiol 51(3):957–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00263-8
Rajput G, Pandya N (2020) Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using gold nanoparticles capped by polyoxyethylene cholesteryl ether. Adv Sci Eng Med 12(10):1236–1240. https://doi.org/10.1166/asem.2020.2679
Revie NM, Iyer KR, Robbins N, Cowen LE (2018) Antifungal drug resistance: evolution, mechanisms and impact. Curr Opin Microbiol 45:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2018.02.005
Rónavári A, Igaz N, Gopisetty MK, Szerencsés B, Kovács D, Papp C, Vágvölgyi C, Boros I, Kónya Z, Kiricsi M, Pfeiffer I (2018) Biosynthesized silver and gold nanoparticles are potent antimycotics against opportunistic pathogenic yeasts and dermatophytes. Int J Nanomedicine 13:695–703. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s152010
Saravanan A, Kumar PS, Karishma S, Vo DVN, Jeevanantham S, Yaashikaa PR, George CS (2021) A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 264:128580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128580
Sawant AM, Vankudoth R, Navale V, Kumavat R, Kumari P, Santhakumari B, Vamkudoth KR (2019) Morphological and molecular characterization of Penicillium rubens sp. nov isolated from poultry feed. Indian Phytopathol 72(3):461–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00165-2
Sellamani M, Kalagatur NK, Siddaiah C, Mudili V, Krishna K, Natarajan G, Rao Putcha VL (2016) Antifungal and zearalenone inhibitory activity of Pediococcus pentosaceus isolated from dairy products on Fusarium graminearum. Front Microbiol 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00890
Sheikh H, Awad MF (2022) Biogenesis of nanoparticles with inhibitory effects on aflatoxin B1 production by Aspergillus flavus. Electron J Biotechnol 60:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2022.09.003
Soenen SJ, Manshian BB, Abdelmonem AM, Montenegro JM, Tan S, Balcaen L, Vanhaecke F, Brisson AR, Parak WJ, De Smedt SC, Braeckmans K (2014) The cellular interactions of PEGylated gold nanoparticles: effect of PEGylation on cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Part Part Syst Charact 31(7):794–800. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201300357
Srinath BS, Ganesh SG, Rajesh PS, Byrappa K (2022). Mycosynthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles using Penicillium sp for bromothymol blue degradation. Biomed [Internet]. 39(2):346–52. https://doi.org/10.51248/.v39i2.206
Tao C (2018) Antimicrobial activity and toxicity of gold nanoparticles: research progress, challenges and prospects. Lett Appl Microbiol 67(6):537–543. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13082
Ucar D, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I (2017) An overview of electron acceptors in microbial fuel cells. Front Microbiol 19(8):643. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00643
Umamaheswari C, Lakshmanan A, Nagarajan NS (2018) Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic degradation studies of gold nanoparticles against Congo red and methyl orange. Photochem Photobiol B Biol 178:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.10.017
Wahab AK, Nadeem MA, Idriss H (2019). Hydrogen Production During Ethylene Glycol Photoreactions Over Ag-Pd/TiO2 at Different Partial Pressures of Oxygen. Front Chem 22;7:780. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00780
Wang Y, You LX, Zhong HL, Wu GK, Li YP, Yang XJ, Wang AJ, Nealson KH, Herzberg M, Rensing C (2022) Au(III)-induced extracellular electron transfer by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC for the bio-recovery of gold nanoparticles. Environ Res 210:112910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112910
Wu X, Zhao F, Rahunen N, Varcoe JR, Avignone-Rossa C, Thumser AE, Slade RC (2011) A role for microbial palladium nanoparticles in extracellular electron transfer. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(2):427–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201002951
Yassin MA, Elgorban AM, El-Samawaty AERMA, Almunqedhi BMA (2021) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Penicillium verrucosum and analysis of their antifungal activity. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(4):2123–2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.063
You LX, Pan DM, Chen NJ, Lin WF, Chen QS, Rensing C, Zhou SG (2019) Extracellular electron transfer of Enterobacter cloacae SgZ-5T via bimediators for the biorecovery of palladium as nanorods. Environ Int 123:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.018
Yu Q, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Li M (2016) Inhibition of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) on pathogenic biofilm formation and invasion to host cells. Sci Rep 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26667
Zangeneh MM, Bovandi S, Gharehyakheh S, Zangeneh A, Irani P (2019) Green synthesis and chemical characterization of silver nanoparticles obtained using Allium saralicum aqueous extract and survey of in vitro antioxidant, cytotoxic, antibacterial and antifungal properties. Appl Organomet Chem 33(7) Portico. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4961
Zhang X, Li G, Wu D, Liu J, Wu Y (2020) Recent advances on emerging nanomaterials for controlling the mycotoxin contamination: from detection to elimination. Food Frontiers 1(4):360–381. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1002/fft2.42
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India, for providing necessary facilities.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, India (BT/PR27494/NNT/28/1549/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
• Conception and design of study: B. Yogesh, V. Koteswara Rao, C.P. Bhushan.
• Data acquisition: B. Yogesh, V. Sanjana, B. Sreelatha, V. Koteswara Rao
• Data analysis and/or interpretation: B. Yogesh, V. Sanjana, S. Amol, B. Sreelatha, J. Neha
• Writing—original draft: B. Yogesh, V. Koteswara Rao
• Writing—review and editing: V. Koteswara Rao, C.P. Bhushan
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This present material is original work of the authors, and has not been previously published elsewhere.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhandari, Y., Varma, S., Sawant, A. et al. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Penicillium rubens and catalytic detoxification of ochratoxin A and organic dye pollutants. Int Microbiol 26, 765–780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00341-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00341-5