Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between miR-141-3p and B lymphocyte-2 gene (Bcl2) gene and its biological behavior on colon cancer cell line SW480.
Methods
qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression level of miR-141-3p in colon cancer tissues and adjacent tissues, as well as in colon cancer cell line and normal human colonic epithelial cell line FHC. MTT assay, wound assay, and Transwell demonstrated the effects of miR-141-3p on colon cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. Targetscan7.1 predictive software and dual luciferase reporter assays were used to detect the targeted regulation of miR-141-3p on the apoptosis-related gene Bcl2. MTT assay, wound assay, Transwell and flow cytometry were used to detect the effect of Bcl2 on miR-141-3p on colon cancer proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis.
Results
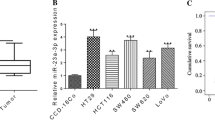
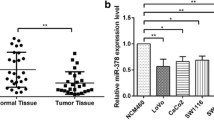
Compared with adjacent tissues, the expression of miR-141-3p in colon cancer tissues was significantly down-regulated. Colon cancer patients with low expression of miR-141-3p had poorer prognosis. Compared with normal colonic epithelial cells, miR-141-3p expression was significantly down-regulated in colon cancer cell lines, and overexpression of miR-141-3p significantly attenuated the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells. Knockdown of miR-141-3p significantly promoted the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells. miR-141-3p targets the negative regulation of Bcl2. Knockdown of Bcl2 significantly attenuated the promotion of miR-141-3p inhibitor on proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells and inhibition of apoptosis. Knockdown of Bcl2 significantly enhanced the inhibition effect of miR-141-3p inhibitor on proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells.
Conclusions
In conclusion, miR-141-3p can inhibit the cancer by regulating Bcl2, and miR-141-3p has the potential to become a potential therapeutic target for colon cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Lee ES. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2016. Cancer Res Treat. 2019;51:417–30.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30.
Scheer A, Auer RA. Surveillance after curative resection of colorectal cancer. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:242–50.
Van Cutsem E, Nordlinger B, Cervantes A, Group EGW. Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for treatment. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:v93–7.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–991.
Xu M, Duan Y, Xiao J. Exercise improves the function of endothelial cells by microRNA. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2019;12:391–3.
Aryal B, Rotllan N, Fernandez-Hernando C. Noncoding RNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014;16:40.
Ambros V, Chen X. The regulation of genes and genomes by small RNAs. Development. 2007;134:1635–41.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5.
Carthew R, Sontheimer EJ. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 2009;136:642–55.
Bo X, Chen Y, Sheng W, Gong Y, Wang H, Gao W, Zhang B. The regulation and function of microRNA-377/RASSF8 signaling axis in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:3630–8.
Wei J, Wang Z, Wang Z, Yang Y, Fu C, Zhu J, Jiang D. MicroRNA-31 function as a suppressor was regulated by epigenetic mechanisms in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5348490.
Mao QD, Zhang W, Zhao K, Cao B, Yuan H, Wei LZ, Song MQ, Liu XS. MicroRNA-455 suppresses the oncogenic function of HDAC2 in human colorectal cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017;50:6103.
Ghorbanmehr N, Gharbi S, Korsching E, Tavallaei M, Einollahi B, Mowla SJ. miR-21-5p, miR-141-3p, and miR-205-5p levels in urine-promising biomarkers for the identification of prostate and bladder cancer. Prostate. 2019;79:88–95.
Li W, Cui Y, Wang D, Wang Y, Wang L. MiR-141-3p functions as a tumor suppressor through directly targeting ZFR in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;509:647–55.
Fang M, Huang W, Wu X, Gao Y, Ou J, Zhang X, Li Y. MiR-141-3p suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer via targeting Yin Yang 1. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019;302:258–68.
Zhou Y, Zhong JH, Gong FS, Xiao J. MiR-141-3p suppresses gastric cancer induced transition of normal fibroblast and BMSC to cancer-associated fibroblasts via targeting STAT4. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;107:85–94.
Liu CZ, Ye ZH, Ma J, He RQ, Liang HW, Peng ZG, Chen G. A qRT-PCR and gene functional enrichment study focused on downregulation of miR-141-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017;2017:1533034617705056.
Cui HW, Han WY, Hou LN, Yang L, Li X, Su XL. miR-1915-3p inhibits Bcl2 expression in the development of gastric cancer. Biosci Rep. 2019;39
Koyama K, Katsurada N, Jimbo N, et al. Overexpression of CD 133 and BCL2 in non-small cell lung cancer with neuroendocrine differentiation after transformation in ALK rearrangement-positive adenocarcinoma. Pathol Int. 2019;69:294–9.
Turker P, Segersten U, Malmstrom PU, Hemdan T. Is Bcl2 a predictive marker of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with urothelial bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy? Scand J Urol. 2019;53:45–50.
Warren CFA, Wong-Brown MW, Bowden NA. BCL2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:177.
Strand SH, Bavafaye-Haghighi E, Kristensen H, Rasmussen AK, Hoyer S, Borre M, Mouritzen P, Besenbacher S, Orntoft TF, Sorensen KD. A novel combined miRNA and methylation marker panel (miMe) for prediction of prostate cancer outcome after radical prostatectomy. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:3445–52.
Kim EG, Kim JO, Park HS, Ryu CS, Oh J, Jun HH, Kim JW, Kim NK. Genetic associations between the miRNA polymorphisms miR-130b (rs373001), miR-200b (rs7549819), and miR-495 (rs2281611) and colorectal cancer susceptibility. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:480.
Seo HA, Hwang CY, Moeng S, Park JK. an in vitro protocol for evaluating microRNA levels, functions, and associated target genes in tumor cells. J Vis Exp. 2019.
Youness RA, Hafez HM, Khallaf E, Assal RA, Abdel Motaal A, Gad MZ. The long noncoding RNA sONE represses triple-negative breast cancer aggressiveness through inducing the expression of miR-34a, miR-15a, miR-16, and let-7a. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:20286–97.
Patel N, Garikapati KR, Pandita RK, Singh DK, Pandita TK, Bhadra U, Bhadra MP. miR-15a/miR-16 down-regulates BMI1, impacting Ub-H2A mediated DNA repair and breast cancer cell sensitivity to doxorubicin. Sci Rep. 2017;7:4263.
Wang M, Hu M, Li Z, Qian D, Wang B, Liu DX. miR-141-3p functions as a tumor suppressor modulating activating transcription factor 5 in glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490:1260–7.
Li JH, Zhang Z, Du MZ, Guan YC, Yao JN, Yu HY, Wang BJ, Wang XL, Wu SL, Li Z. microRNA-141-3p fosters the growth, invasion, and tumorigenesis of cervical cancer cells by targeting FOXA2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;657:23–30.
Liu F, Wang W, Li S, Yang Q, Hu J, Zeng N, Gao C. MicroRNA 141 represses nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth through inhibiting BMI1. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:6479–87.
Mak CS, Yung MM, Hui LM, et al. MicroRNA-141 enhances anoikis resistance in metastatic progression of ovarian cancer through targeting KLF12/Sp1/survivin axis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:11.
Choi SK, Kim HS, Jin T, Hwang EH, Jung M, Moon WK. Overexpression of the miR-141/200c cluster promotes the migratory and invasive ability of triple-negative breast cancer cells through the activation of the FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways by secreting VEGF-A. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:570.
Huang S, Wa Q, Pan J, Peng X, Ren D, Huang Y, Chen X, Tang Y. Downregulation of miR-141-3p promotes bone metastasis via activating NF-kappaB signaling in prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:173.
Mohamed MS, Abdelhamid AO, Almutairi FM, Ali AG, Bishr MK. Induction of apoptosis by pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridazine derivative in lung cancer cells via disruption of Bcl2/Bax expression balance. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018;26:623–9.
Alarifi S, Ali H, Alkahtani S, Alessia MS. Regulation of apoptosis through Bcl2/bax proteins expression and DNA damage by nano-sized gadolinium oxide. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:4541–51.
Missaoui N, Landolsi H, Mestiri S, Essakly A, Abdessayed N, Hmissa S, Mokni M, Yacoubi MT. Immunohistochemical analysis of c-erbB-2, Bcl2, p53, p21(WAF1/Cip1), p63 and Ki-67 expression in hydatidiform moles. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215:446–52.
Li M, Long C, Yang G, Luo Y, Du H. MiR-26b inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and enhances apoptosis by suppressing TRAF5-mediated MAPK activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;471:361–7.
Iglesias-Figueroa BF, Siqueiros-Cendón TS, Gutierrez DA, Aguilera RJ, Espinoza-Sánchez EA, Arévalo-Gallegos S, Varela-Ramirez A, Rascón-Cruz Q. Recombinant human lactoferrin induces apoptosis, disruption of F-actin structure and cell cycle arrest with selective cytotoxicity on human triple negative breast cancer cells. Apoptosis. 2019;24:562–77.
Wang N, Li P, Liu W, Wang N, Lu Z, Feng J, Zeng X, Yang J, Wang Y, Zhao W. miR-141-3p suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting GLI2 in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:747–54.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Incentive Project of Qiqihar City (CSFGG-2020166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST and SL conceived and designed the study, and drafted the manuscript. ST, XZ, HG, JY and YQ collected, analyzed and interpreted the experimental data. XZ and SL revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Ethical Committee of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihaer Medical University and conducted in accordance with the ethical standards.
Informed consent
Subjects signed the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, .J., Zhang, X.Y., Guo, H.F. et al. Study on effects of miR-141-3p in proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of colon cancer cells by inhibiting Bcl2. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 2526–2535 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02653-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02653-2