Abstract
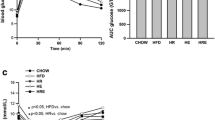
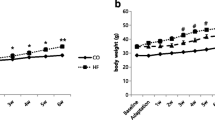
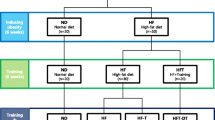
To explore the effects of rutin and exercise on high-fat diet (HFD)-induced disrupted lipolytic signaling, adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 (TRPV4) and its associated protein expression, and whether depot-specific effects existed. C57BL/6J mice were randomized into five groups: chow group, HFD, HFD plus rutin intervention group (HR), HFD combined with treadmill running group (HE), and HFD combined with treadmill running and rutin intervention group (HRE). At the end of the 16-week intervention, lipolytic markers, AMPK signaling pathways, TRPV4, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α + β (PGC-1α + β) from adipose tissue were measured by western blotting. In epididymal adipose tissue, HFD resulted in significant reduction in the phosphorylation of hormone sensitive lipase at serine660 (p-HSL660), perilipin A, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), p-AMPK, and p-acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) protein expression. Exercise intervention and exercise plus rutin completely restored p-HSL660, perilipin A, PEPCK, p-AMPK, and p-ACC protein expression to normal level. HFD and HR groups have reduced expression of PGC-1α + β, exercise, and exercise plus rutin completely restored PGC-1α + β expression to normal level. In subcutaneous adipose tissue, HFD elevated TRPV4, exercise, and exercise plus rutin completely reduced TRPV4 to normal level. HR, HE, and HRE group have increased PGC-1α + β. In conclusion, depot-specific effects existed in regards to how rutin and exercise affect lipolytic signaling and p-AMPK, as well as TRPV4 and PGC-1α + β expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthonsen MW, Ronnstrand L, Wernstedt C, Degerman E, Holm C (1998) Identification of novel phosphorylation sites in hormone-sensitive lipase that are phosphorylated in response to isoproterenol and govern activation properties in vitro. J Biol Chem 273:215–221
Bishnoi M, Kondepudi KK, Gupta A, Karmase A, Boparai RK (2013) Expression of multiple transient receptor potential channel genes in murine 3T3-L1 cell lines and adipose tissue. Pharmacol Rep 65:751–755
Castellani L, Root-Mccaig J, Frendo-Cumbo S (1985) Beaudoin MS, and Wright DC (2014) Exercise training protects against an acute inflammatory insult in mouse epididymal adipose tissue. J Appl Physiol 116:1272–1280
Chen N, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Xu J, Wan Z, Qin L (2014) Resistin induces lipolysis and suppresses adiponectin secretion in cultured human visceral adipose tissue. Regul Pept 194–195:49–54
de Farias JM, Bom KF, Tromm CB, Luciano TF, Marques SO, Tuon T, Silva LA, Lira FS, de Souza CT, Pinho RA (2013) Effect of physical training on the adipose tissue of diet-induced obesity mice: interaction between reactive oxygen species and lipolysis. Horm Metab Res 45:190–196
Gaidhu MP, Anthony NM, Patel P, Hawke TJ, Ceddia RB (2010) Dysregulation of lipolysis and lipid metabolism in visceral and subcutaneous adipocytes by high-fat diet: role of ATGL, HSL, and AMPK. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C961–C971
Gaidhu MP, Fediuc S, Anthony NM, So M, Mirpourian M, Perry RL, Ceddia RB (2009) Prolonged AICAR-induced AMP-kinase activation promotes energy dissipation in white adipocytes: novel mechanisms integrating HSL and ATGL. J Lipid Res 50:704–715
Gao M, Ma Y, Liu D (2013) Rutin suppresses palmitic acids-triggered inflammation in macrophages and blocks high fat diet-induced obesity and fatty liver in mice. Pharm Res 30:2940–2950
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:367–377
Hickner RC, Kemeny G, Clark PD, Galvin VB, McIver KL, Evans CA, Carper MJ, Garry JP (2012) In vivo nitric oxide suppression of lipolysis in subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue is greater in obese than lean women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20:1174–1178
Huijsman E, van de Par C, Economou C, van der Poel C, Lynch GS, Schoiswohl G, Haemmerle G, Zechner R, Watt MJ (2009) Adipose triacylglycerol lipase deletion alters whole body energy metabolism and impairs exercise performance in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E505–E513
Ibrahim MM (2010) Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes Rev 11:11–18
Jaworski K, Ahmadian M, Duncan RE, Sarkadi-Nagy E, Varady KA, Hellerstein MK, Lee HY, Samuel VT, Shulman GI, Kim KH, de Val S, Kang C, Sul HS (2009) AdPLA ablation increases lipolysis and prevents obesity induced by high-fat feeding or leptin deficiency. Nat Med 15:159–168
Jun JK, Lee WL, Park HG, Lee SK, Jeong SH, Lee YR (2014) Moderate intensity exercise inhibits macrophage infiltration and attenuates adipocyte inflammation in ovariectomized rats. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem 18:119–127
Kuntic V, Pejic N, Ivkovic B, Vujic Z, Ilic K, Micic S, Vukojevic V (2007) Isocratic RP-HPLC method for rutin determination in solid oral dosage forms. J Pharm Biomed Anal 43:718–721
Langin D, Dicker A, Tavernier G, Hoffstedt J, Mairal A, Ryden M, Arner E, Sicard A, Jenkins CM, Viguerie N, van Harmelen V, Gross RW, Holm C, Arner P (2005) Adipocyte lipases and defect of lipolysis in human obesity. Diabetes 54:3190–3197
Lass A, Zimmermann R, Haemmerle G, Riederer M, Schoiswohl G, Schweiger M, Kienesberger P, Strauss JG, Gorkiewicz G, Zechner R (2006) Adipose triglyceride lipase-mediated lipolysis of cellular fat stores is activated by CGI-58 and defective in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. Cell Metab 3:309–319
Mauriege P, Galitzky J, Berlan M, Lafontan M (1987) Heterogeneous distribution of beta and alpha-2 adrenoceptor binding sites in human fat cells from various fat deposits: functional consequences. Eur J Clin Invest 17:156–165
Moghbelinejad S, Nassiri-Asl M, Farivar TN, Abbasi E, Sheikhi M, Taghiloo M, Farsad F, Samimi A, Hajiali F (2014) Rutin activates the MAPK pathway and BDNF gene expression on beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Lett 224:108–113
Nielsen TS, Jessen N, Jorgensen JO, Moller N, Lund S (2014) Dissecting adipose tissue lipolysis: molecular regulation and implications for metabolic disease. J Mol Endocrinol 52:R199–R222
O’Conor CJ, Griffin TM, Liedtke W, Guilak F (2013) Increased susceptibility of Trpv4-deficient mice to obesity and obesity-induced osteoarthritis with very high-fat diet. Ann Rheum Dis 72:300–304
Shen WJ, Patel S, Natu V, Kraemer FB (1998) Mutational analysis of structural features of rat hormone-sensitive lipase. Biochemistry 37:8973–8979
Srivastava S, Barrett JN, Moraes CT (2007) PGC-1alpha/beta upregulation is associated with improved oxidative phosphorylation in cells harboring nonsense mtDNA mutations. Hum Mol Genet 16:993–1005
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:695–702
Sutherland LN, Bomhof MR, Capozzi LC, Basaraba SA, Wright DC (2009) Exercise and adrenaline increase PGC-1{alpha} mRNA expression in rat adipose tissue. J Physiol 587:1607–1617
Thodeti CK, Matthews B, Ravi A, Mammoto A, Ghosh K, Bracha AL, Ingber DE (2009) TRPV4 channels mediate cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell reorientation through integrin-to-integrin signaling. Circ Res 104:1123–1130
Wan Z, Root-McCaig J, Castellani L, Kemp BE, Steinberg GR, Wright DC (2014) Evidence for the role of AMPK in regulating PGC-1 alpha expression and mitochondrial proteins in mouse epididymal adipose tissue. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22:730–738
Wan Z, Thrush AB, Legare M, Frier BC, Sutherland LN, Williams DB, Wright DC (2010) Epinephrine-mediated regulation of PDK4 mRNA in rat adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1162–C1170
Ye L, Kleiner S, Wu J, Sah R, Gupta RK, Banks AS, Cohen P, Khandekar MJ, Bostrom P, Mepani RJ, Laznik D, Kamenecka TM, Song X, Liedtke W, Mootha VK, Puigserver P, Griffin PR, Clapham DE, Spiegelman BM (2012) TRPV4 is a regulator of adipose oxidative metabolism, inflammation, and energy homeostasis. Cell 151:96–110
Zhang LP, Ma F, Abshire SM, Westlund KN (2013) Prolonged high fat/alcohol exposure increases TRPV4 and its functional responses in pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 304:R702–R711
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81472975 to Wan Z. and grant no. 81273067 to Qin L.) and Jiangsu Province Preventive Medical Program “Establishing the system of all of the subtype complete genome of the influenza: a virus” (program no. Y2012008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Cheng, J., Zhou, L. et al. Effects of treadmill running and rutin on lipolytic signaling pathways and TRPV4 protein expression in the adipose tissue of diet-induced obese mice. J Physiol Biochem 71, 733–742 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0437-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0437-5