Abstract
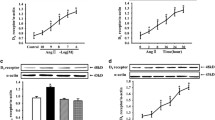
Dopamine and urodilatin promote natriuresis and diuresis through a common pathway that involves reversible deactivation of renal Na+, K+-ATPase. We have reported that urodilatin enhances dopamine uptake in outer renal cortex through the natriuretic peptide type A receptor. Moreover, urodilatin enhances dopamine-induced inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity. The objective of the present work was to investigate the intracellular signals involved in urodilatin effects on dopamine uptake in renal cortex of kidney rats. We show that urodilatin-elicited increase in 3H-dopamine was blunted by methylene blue (10 μM), a non-specific guanylate cyclase inhibitor, and by phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (1 μM), a particulate guanylate cyclase inhibitor, but not by 1H-[1,2,4]-Oxadiazolo-[4,3-a]-quinoxalin-1-one (10 μM), a specific soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitor; therefore the involvement of particulate guanylate cyclase on urodilatin mediated dopamine uptake was confirmed. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate and proteinkinase G were also implicated in the signaling pathway, since urodilatin effects were mimicked by the analog 125 μM 8-Br-cGMP and blocked by the proteinkinase G-specific inhibitor, KT-5823 (1 μM). In conclusion, urodilatin increases dopamine uptake in renal cortex stimulating natriuretic peptide type A receptor, which signals through particulate guanylate cyclase activation, cyclic guanosine monophosphate generation, and proteinkinase G activation. Dopamine and urodilatin may achieve their effects through a common pathway that involves deactivation of renal Na+, K+-ATPase, reinforcing their natriuretic and diuretic properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brismar H, Holtbäck U, Aperia A (2000) Mechanisms by which intrarenal dopamine and ANP interact to regulate sodium metabolism. Clin Exp Hypertens 22:303–307
Carranza A, Nowicki S, Barontini M, Armando I (2000) l-DOPA uptake and dopamine production in proximal tubular cells are regulated by β2-adrenergic receptors. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 279:77–83
Ciarimboli G, Schlatter E (2005) Regulation of organic cation transport. Pflugers Arch 449:423–441
Citarella MR, Choi MR, Gironacci MM, Medici C, Correa AH, Fernández BE (2009) Urodilatin and dopamine: a new interaction in the kidney. Regul Pept 153:19–24
Correa AH, Choi MR, Gironacci M, Valera MS, Fernández BE (2007) Signaling pathways involved in atrial natriuretic factor and dopamine regulation of renal Na+, K+ -ATPase activity. Regul Pept 138:26–31
Eisenhofer G (2001) The role of neuronal and extraneuronal plasma membrane transporters in the inactivation of peripheral catecholamines. Pharmacol Ther 91:35–62
Féraille E, Doucet A (2001) Sodium-potassium-adenosinetriphosphatase-dependent sodium transport in the kidney: hormonal control. Physiol Rev 81:345–418
Fernández BE, Correa AH, Choi MR (2005) Atrial natriuretic factor stimulates renal dopamine uptake mediated by natriuretic peptide-type A receptor. Regul Pept 124:137–144
Hirsch JR, Meyer M, Forssmann WG (2006) ANP and urodilatin: who is who in the kidney. Eur J Med Res 11:447–454
Hussain T, Lokhandwala MF (2003) Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. Exp Biol Med 228:134–142
Itaba S, Chijiiwa Y, Matsuzaka H, Motomura Y, Nawata H (2004) Presence of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) in guinea pig caecum: role and mechanisms of CNP in circular smooth muscle relaxation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:375–382
Jose PA, Eisner GM, Felder RA (2000) Renal dopamine and sodium homeostasis. Curr Hypertens Rep 2:174–183
Jose PA, Eisner GM, Felder RA (2002) Dopamine receptor-coupling defect in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 4:237–244
Pietig G, Mehrens T, Hirsch JR, Cetinkaya I, Piechota H, Schlatter E (2001) Properties and regulation of organic cation transport in freshly isolated human proximal tubules. J Biol Chem 276:33741–33746
Schulz-Knappe P, Forssmann K, Herbst F, Hock D, Pipkorn R, Forssmann W-G (1988) Isolation and structural analysis of “urodilatin”, a new peptide of the cardiodilatin-(ANP)-family, extracted from human urine. Klin Wochenschr 66:752–759
Urakami Y, Okuda M, Masuda S, Akazawa M, Saito H, Inui K (2001) Distinct characteristics of organic cations transporters, OCT1 and OCT2, in the basolateral membrane of renal tubules. Pharm Res 18:1528–1534
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas de la Republica Argentina (CONICET PIP 1337), PICT 05-13775 ANPCYT and Universidad de Buenos Aires (20020090300090 and B113). We would like to thank Dr. Gabriela Acosta and Vanesa Turco for their excellent technical support and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Marcelo R. Choi and Marisa R. Citarella contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, M.R., Citarella, M.R., Lee, B.M. et al. Urodilatin increases renal dopamine uptake: intracellular network involved. J Physiol Biochem 67, 243–247 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-010-0069-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-010-0069-8